参考
代码地址:
https://github.com/viakiba/viakiba/tree/master/rsa_sign_demo
参考:
签名
http://dikar.iteye.com/blog/1231184
https://q.cnblogs.com/q/93977
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/33305800/difference-between-sha256withrsa-and-sha256-then-rsa
http://8btc.com/thread-155281-1-1.html
https://blog.csdn.net/kongqz/article/details/6305548
摘要
https://www.cnblogs.com/fishou/p/4159092.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/huhx/p/messageDigest.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/jingmoxukong/p/5700906.html
消息签名
众所周知,公钥是可以公布出去,私钥只能自己留存得到妥善安全不可泄漏的保管。我们使用RSA证书一般是用于加解密使用的,即 公钥对消息进行加密,只有私钥才能对消息进行解密。这样很大的程度上就保证了数据的不被第三方查看。对应的,如果使用私钥对消息使用算法得到消息的摘要一并发送给接收者,接收者使用公钥对消息和摘要进行验证即可保证消息不被篡改同时保证接收到的消息来自被信任的发送方。这就是消息签名。这一片文章主要介绍java里如何进行消息的签名与验签。
消息摘要
(1)唯一性:数据只要有一点改变,那么再通过消息摘要算法得到的摘要也会发生变化。虽然理论上有可能会发生碰撞,但是概率极其低。
(2)不可逆:消息摘要算法的密文无法被解密。
(3)不需要密钥,可使用于分布式网络。
(4)无论输入的明文有多长,计算出来的消息摘要的长度总是固定的。
原理
消息摘要,其实就是将需要摘要的数据作为参数,经过哈希函数(Hash)的计算,得到的散列值
准备
我们需要生成一对公私钥进行进行接下来的实践操作。借助openssl可以完成需求。这一步只是生成所需要的证书,不会对生成证书做深入探讨。
openSSl 方式
//生成一个私钥 2048位
openssl genrsa -out rsa_private.key 2048
//使用私钥生成对应的公钥
openssl rsa -in rsa_private.key -pubout -out rsa_public.key
//解析第一步生成的私钥
openssl rsa -in rsa_private.key -noout -text
如图所示:
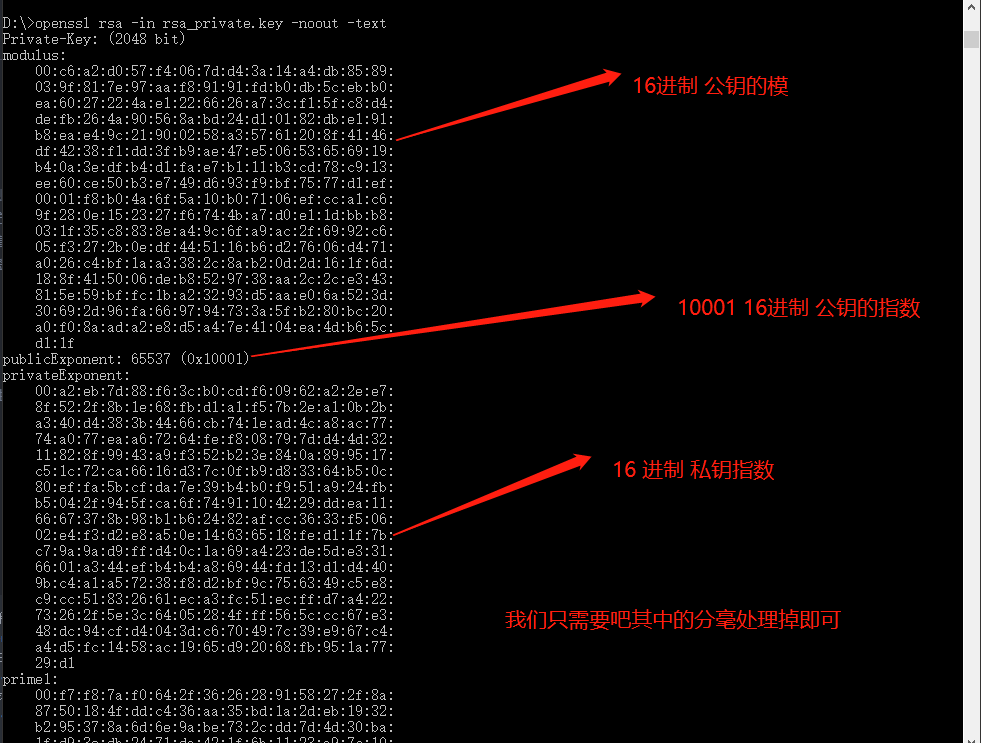 处理后的值如下:
处理后的值如下:
modulus : 00c6a2d057f4067dd43a14a4db8589039f817e97aaf89191fdb0db5cebb0ea6027224ae1226626a73cf15fc8d4defb264a90568abd24d10182dbe191b8eae49c21900258a35761208f4146df4238f1dd3fb9ae47e50653656919b40a3edfb4d1fae7b111b3cd78c913ee60ce50b3e749d693f9bf7577d1ef0001f8b04a6f5a10b07106efcca1c69f280e152327f6744ba7d0e11dbbb8031f35c8838ea49c6fa9ac2f6992c605f3272b0edf445116b6d27606d471a026c4bf1aa3382c8ab20d2d161f6d188f415006deb8529738aa2c2ce343815e59bffc1ba23293d5aae06a523d30692d96fa669794733a5fb280bc20a0f08aada2e8d5a47e4104ea4db65cd11f
publicExponent:10001
privateExponent:00a2eb7d88f63cb0cdf60962a22ee78f522f8b1e68fbd1a1f57b2ea10b2ba340d4383b4466cb741ead4ca8ac7774a077eaa67264fef808797dd44d3211828f9943a9f352b23e840a899517c51c72ca6616d37c0fb9d83364b50c80effa5bcfda7e39b4b0f951a924fbb5042f945fca6f7491104229ddea116667378b98b1b62482afcc3633f50602e4f3d2e8a50e14636518fed11f7bc79a9ad9ffd40c1a69a423de5de3316601a344efb4b4a86944fd13d1d4409bc4a1a57238f8d2bf9c756349c5e8c9cc51832661eca3fc51ecffd7a42273262f5e3c6405284fff565ccc67e348dc94cfd4043dc670497c39e967c4a4d5fc1458ac1965d92068fb951a7729d1
RSA签名
有哪些算法
RSA证书签名算法和填充模式组合后再加上不同时期的ISO约定的规范,得到的种类太多太多了,完全写出来是不可能的,太多了。有多少呢,加上BC扩展的可以使用如下代码得到:
//测试执行的类中 static 要添加以下的支持,此处说明后,后续不再写出。
static {
Security.addProvider(new BouncyCastleProvider());
}
@Test
public void getAllAlg(){
//这里可以拿到jdk与bc扩展支持的所有与安全有关的算法
for (Provider provider : Security.getProviders()){
System.out.println("Provider: " + provider.getName());
for (Provider.Service service : provider.getServices()){
System.out.println(" Algorithm Pattern: " + service);
}
System.out.println("\n");
}
//所有结果可以查看以下连接
// https://github.com/viakiba/viakiba/blob/master/rsa_sign_demo/src/main/resources/allAlg.md
}
//其中关于RSA签名相关的可以根据 Sha1withRsa 关键字进行检索(关联前后结果) 不完全检索结果 查看如下连接
// https://github.com/viakiba/viakiba/blob/master/rsa_sign_demo/src/main/resources/signAlg.md
// 介绍的例子是这些 数字越大生成的签名信息越复杂,签名的复制难度会更高
MD2withRSA MD5withRSA SHA1withRSA SHA224withRSA SHA256withRSA SHA384withRSA SHA512withRSA
//很显然是jdk支持的 不需要BC包 =_=
Provider: SunRsaSign
Algorithm Pattern: SunRsaSign: KeyFactory.RSA -> sun.security.rsa.RSAKeyFactory
Algorithm Pattern: SunRsaSign: KeyPairGenerator.RSA -> sun.security.rsa.RSAKeyPairGenerator
Algorithm Pattern: SunRsaSign: Signature.MD2withRSA -> sun.security.rsa.RSASignature$MD2withRSA
attributes: {SupportedKeyClasses=java.security.interfaces.RSAPublicKey|java.security.interfaces.RSAPrivateKey}
Algorithm Pattern: SunRsaSign: Signature.MD5withRSA -> sun.security.rsa.RSASignature$MD5withRSA
attributes: {SupportedKeyClasses=java.security.interfaces.RSAPublicKey|java.security.interfaces.RSAPrivateKey}
Algorithm Pattern: SunRsaSign: Signature.SHA1withRSA -> sun.security.rsa.RSASignature$SHA1withRSA
attributes: {SupportedKeyClasses=java.security.interfaces.RSAPublicKey|java.security.interfaces.RSAPrivateKey}
Algorithm Pattern: SunRsaSign: Signature.SHA224withRSA -> sun.security.rsa.RSASignature$SHA224withRSA
attributes: {SupportedKeyClasses=java.security.interfaces.RSAPublicKey|java.security.interfaces.RSAPrivateKey}
Algorithm Pattern: SunRsaSign: Signature.SHA256withRSA -> sun.security.rsa.RSASignature$SHA256withRSA
attributes: {SupportedKeyClasses=java.security.interfaces.RSAPublicKey|java.security.interfaces.RSAPrivateKey}
Algorithm Pattern: SunRsaSign: Signature.SHA384withRSA -> sun.security.rsa.RSASignature$SHA384withRSA
attributes: {SupportedKeyClasses=java.security.interfaces.RSAPublicKey|java.security.interfaces.RSAPrivateKey}
Algorithm Pattern: SunRsaSign: Signature.SHA512withRSA -> sun.security.rsa.RSASignature$SHA512withRSA
attributes: {SupportedKeyClasses=java.security.interfaces.RSAPublicKey|java.security.interfaces.RSAPrivateKey}
数据签名
方法如下
/**
* @description 对信息签名
* @date: 21:52 2018/7/28
* @params [plainData 带签名的信息 , radix 证书参数进制, publicModulus 公钥的模, privateExponent 私钥指数, alg 算法名称]
* @return java.lang.String
* @author viakiba
*/
public static String sign(String plainData, int radix, String publicModulus, String privateExponent, String alg) throws Exception {
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance(SignConstants.RSA);
RSAPrivateKeySpec keySpec = new RSAPrivateKeySpec(new BigInteger(publicModulus, radix),
new BigInteger(privateExponent, radix));
PrivateKey privateKey = keyFactory.generatePrivate(keySpec);
Signature signature = Signature.getInstance(alg);
signature.initSign(privateKey);
signature.update(plainData.getBytes(SignConstants.UTF_8));
//签名结果做base64编码
return Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(signature.sign());
}
/**
* @description 验证签名
* @date: 21:52 2018/7/28
* @params [plainData 带签名的信息 , sign 签名结果 , radix 证书参数进制, publicModulus 公钥的模, privateExponent 私钥指数, alg 算法名称]
* @return java.lang.String
* @author viakiba
*/
public static boolean verify(String plainData, String sign, int radix, String publicModulus, String publicExponent, String alg) throws Exception {
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance(SignConstants.RSA);
RSAPublicKeySpec keySpec = new RSAPublicKeySpec(new BigInteger(publicModulus, radix),
new BigInteger(publicExponent, radix));
PublicKey publicKey = keyFactory.generatePublic(keySpec);
final Signature signature = Signature.getInstance(alg);
signature.initVerify(publicKey);
signature.update(plainData.getBytes(SignConstants.UTF_8));
//要对传进的签名结果先做base64解码
return signature.verify(Base64.getDecoder().decode(sign));
}
测试方法
/**
* @description 验证签名算法
* @date: 22:02 2018/7/28
* @params
* @return
* @author viakiba
*/
@Test
public void test2() throws Exception{
String data = "I am vk!";
//SignConstants 有详细的签名算法列表
String alg = SignConstants.SHA256_WITH_RSA;
String signData = SignAndVerify.sign(data, SignConstants.radix_hex,SignConstants.publicModulus,
SignConstants.privateExponent,alg);
log.info(signData);
boolean isOk = SignAndVerify.verify(data,signData,SignConstants.radix_hex,SignConstants.publicModulus,
SignConstants.publicExponent,alg);
log.info(""+isOk);
}
PS: 我们使用的是 SHA256WITHRSA ,对消息进行签名的步骤是,先对消息进行摘要获取 SHA256 算法,然后对消息摘要进行签名。也就是先摘要后签名,因为,在签名数据特别大的情况下,对消息进行签名得到结果的计算零特别大,对消息摘要进行签名可以减少计算量。而且消息摘要本身就可以保证消息完整性。
SHA256WITHRSA 签名步骤就是 (签名说白了就是 使用私钥对消息摘要做加密,使用公钥解密的过程验证的过程。): 对消息字符串用 SHA256 算法取摘要。然后得到的摘要进行二进制编码(der),再对二进制编码后的结果做了一次pad1_5算法填充,得到的结果,用私钥加密。即得到签名结果。